8 The Dispersion of Waves
8.1 THE SUPERPOSITION OF WAVES IN NON-DISPERSIVE MEDIA
8.1.1 Beats

8.1.2 Amplitude modulation of a radio wave
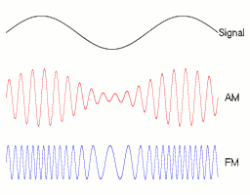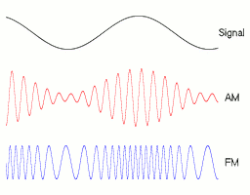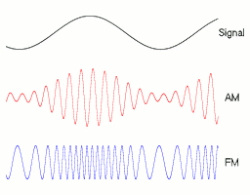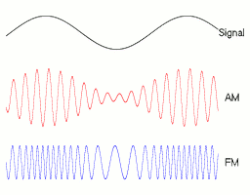



8.2 THE DISPERSION OF WAVES

frequency \(\omega\) is a function of the wavenumber \(k\) :\(\omega=\omega(k)\)
8.2.1 Phase and group velocities


- normal dispersion
- anomalous dispersion
- no dispersion
8.3 THE DISPERSION RELATION
Dispersion of electromagnetic waves occurs in the propagation of radio waves in the ionosphere \[ \omega^2=\omega_0^2+c^2k^2 \] \(\omega_0\):plasma oscillation frequency
For waves on deep water, where the wavelength is small compared with the depth of the water, the angular frequency ω and wavenumber k are related by the dispersion relation \[ \omega^2=gk+\frac{Sk^3}{\rho} \]
8.4 WAVE PACKETS
8.4.1 Formation of a wave packet
bandwidth theorem
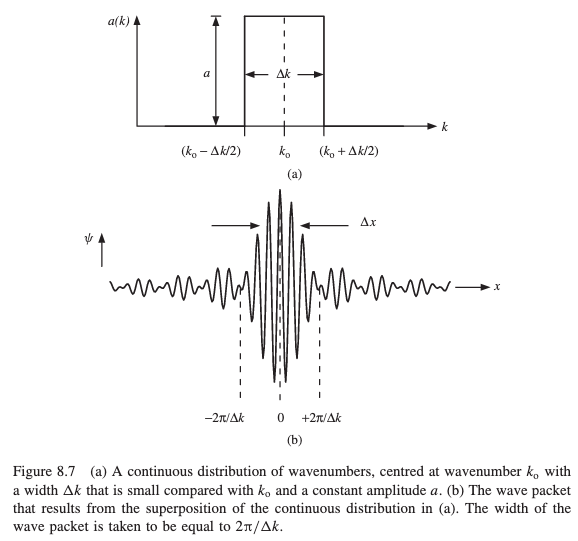 \[
\Delta x \Delta k \approx 2 \pi
\]
\[
\Delta x \Delta k \approx 2 \pi
\] 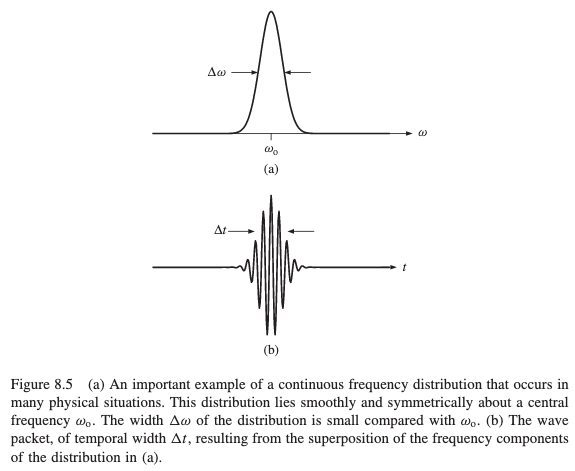 \[
\Delta t \Delta \omega \approx 2 \pi
\] Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
\[
\Delta t \Delta \omega \approx 2 \pi
\] Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle